Job submission#
You can submit Dell Data Processing Engine batch jobs, Spark Connect servers, and Jupyter Notebooks from the Starburst Enterprise web UI. Batch jobs, Spark Connect servers, and Jupyter Notebooks can also be managed programmatically with the CLI.
Batch jobs UI#
Click Spark jobs in the Dell Data Processing Engine section of the Starburst Enterprise web UI to view and manage batch jobs and Spark Connect servers. You must have the Spark runtime UI privilege to access the Spark jobs pane.
The Batch jobs tab shows a list of jobs and information about each job:
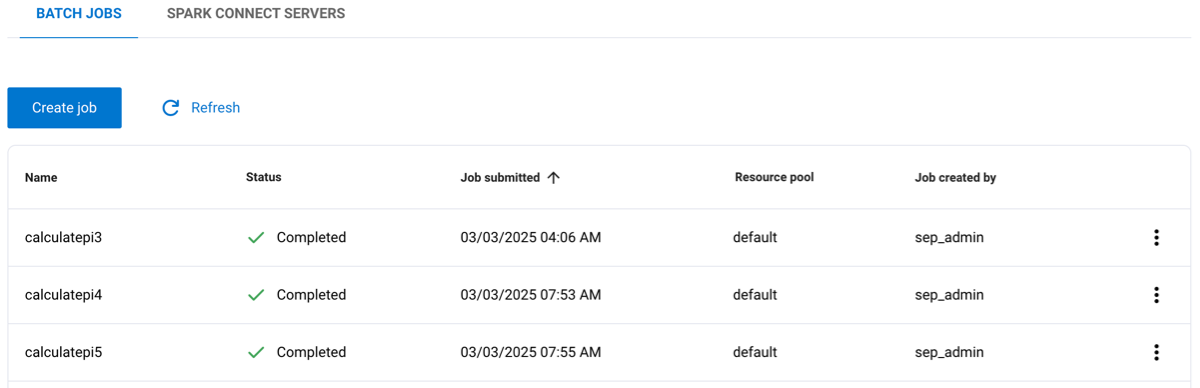
Name: The name given to the job.
Status: The current status of the job, such as completed, running, or pending.
Job submitted: The timestamp for when the job was submitted.
Resource pool: The name of the resource pool assigned to the job.
Job created by: The role that created the job.
Click the Name, Job submitted, or Job created by columns to reorganize the data in ascending or descending order.
The options menu for a Spark job lets you delete the job, download logs, and view the Spark Web UI or Spark History Server UI.
Warning
The Spark History Server UI can take up to 10 seconds to initialize after
you submit a job. If you see an Application not found error message, wait a
few seconds and try again.
Create batch jobs#
To create a Spark batch job:
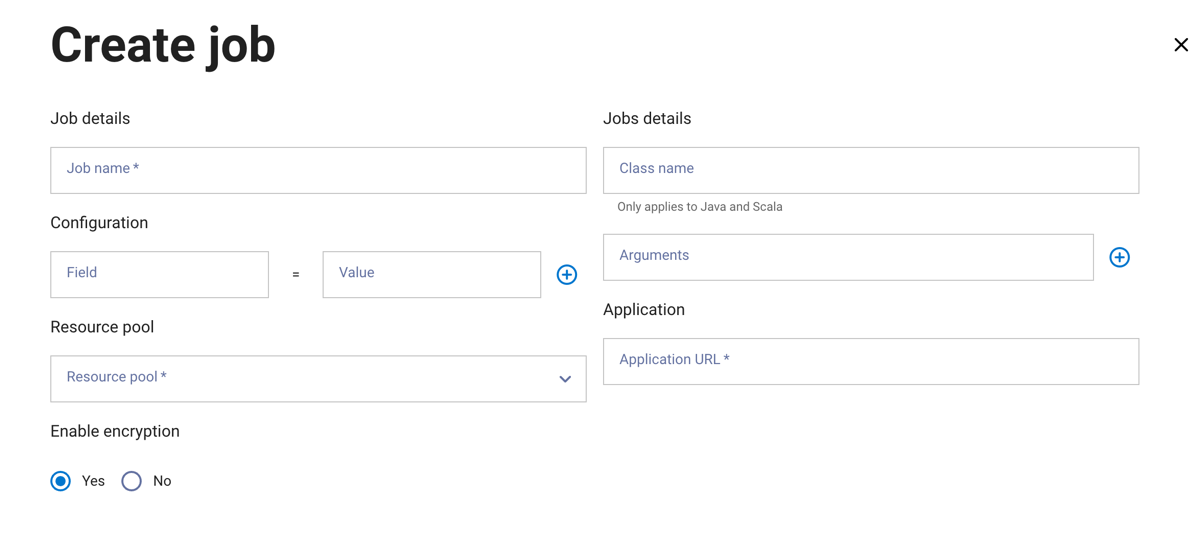
Click Create job.
In the Create job dialog, enter a job name and a class name. The Class name field only applies to Java and Scala configurations and can be left blank if using Python or R. Additionally, arguments can be supplied using the Arguments field.
The Configuration section includes fields to enter properties and their values. Click + to add additional configuration properties.
Select a resource pool to assign to the job.
In the Application section, enter your application’s file path URL.
Choose whether to enable encryption.
Click Next.
Warning
Batch jobs running on a node may fail if the node is rebooted. Automatic failover to another node is not guaranteed.
In the next dialog pane:
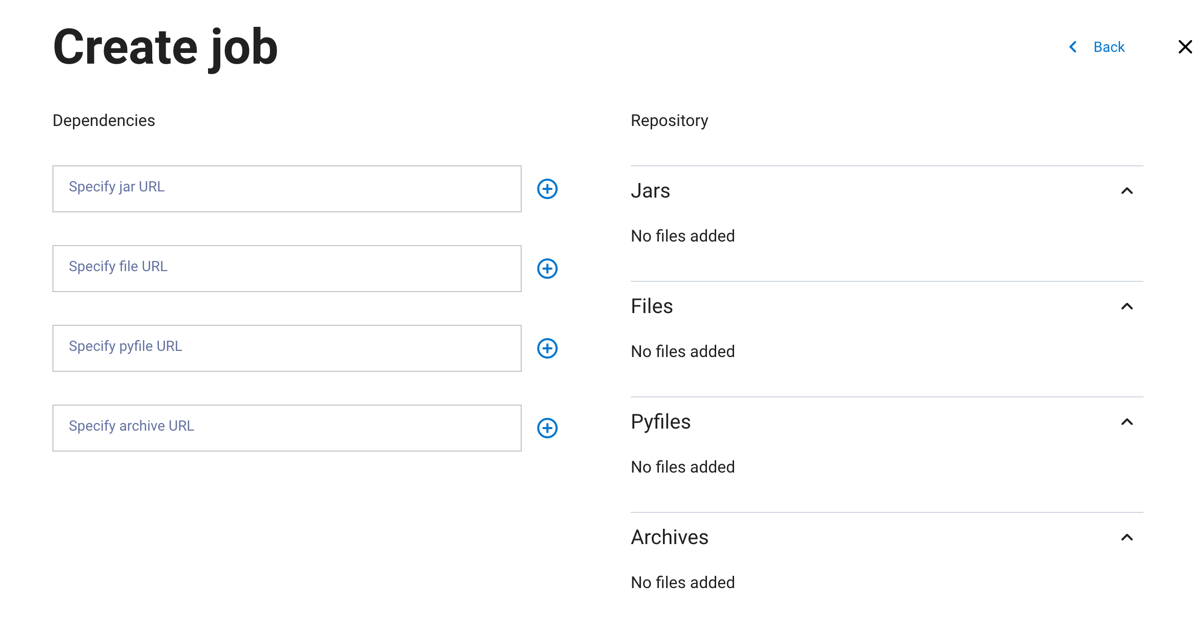
Add the path for your job’s dependencies. Dependencies can be
JAR,FILES,PYFILES, orARCHIVEfiles. Click + to add more dependencies of the same file type. Files are displayed on the right-hand side of the pane.Click Next.
In the next dialog pane:
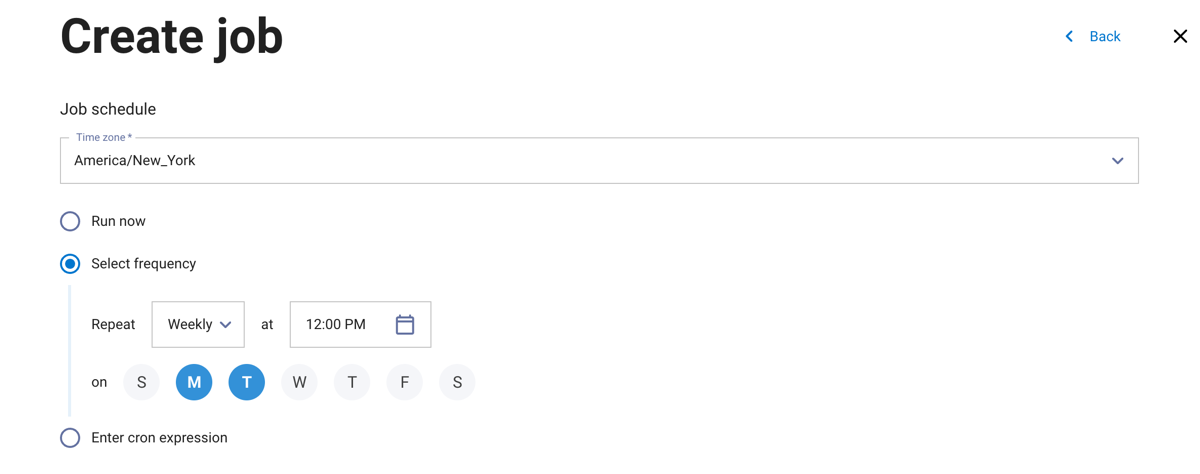
Choose to run the job now or on a recurring schedule. Select a timezone from the drop-down menu, then select a frequency or enter a cron expression to set a schedule for the job to run.
Click Create.
Spark Connect servers#
In the Spark jobs UI pane, click the Spark Connect servers tab to view a list of your existing servers. You must have the Spark runtime UI privilege to access the Spark jobs pane
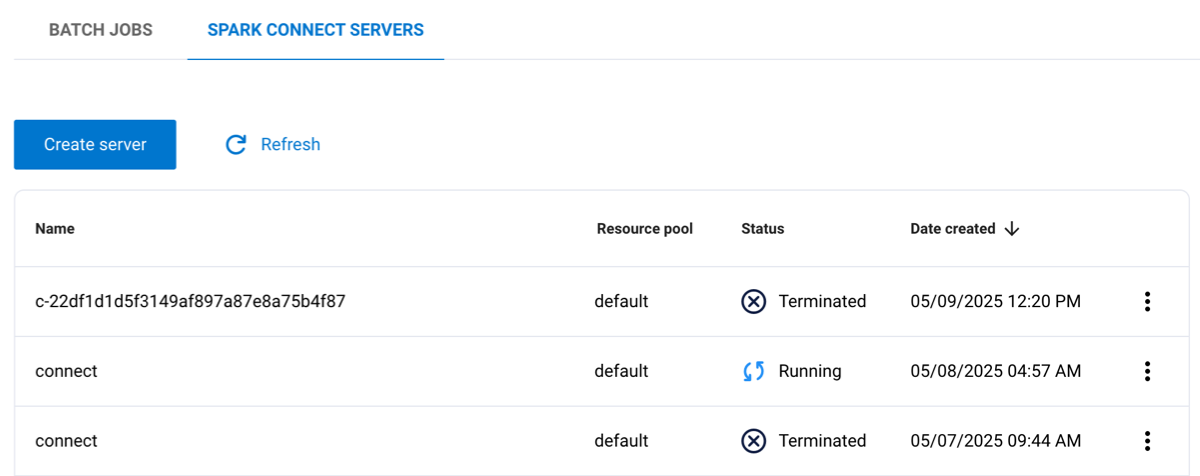
The following columns are listed:
Name: The name given to the server.
Resource pool: The name of the resource pool assigned to the server.
Status: The current status of the server, such as completed or running.
Date created: The timestamp for when the server was created.
Click the options menu for a server to download logs, view the Spark web UI, generate a Spark Connect URL, or delete the server.
Create Spark Connect server#
To create a Spark Connect server:
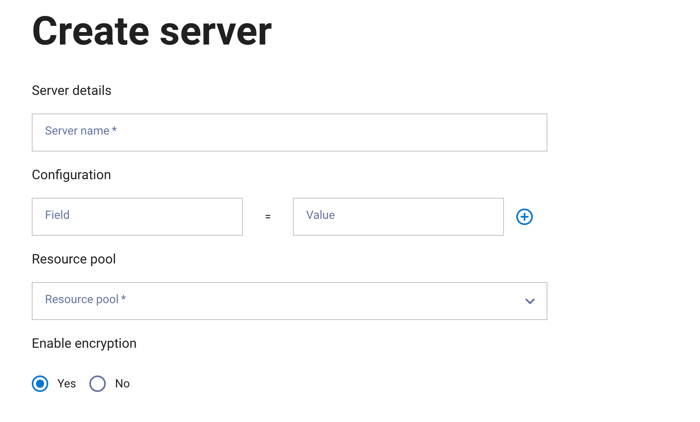
Click Create server.
In the Create server dialog, enter a server name.
The Configuration section includes fields to enter properties and their values. Click + to add additional configuration properties.
Select a resource pool to assign to the server.
Choose whether to enable encryption.
Click Next.
In the next dialog pane:
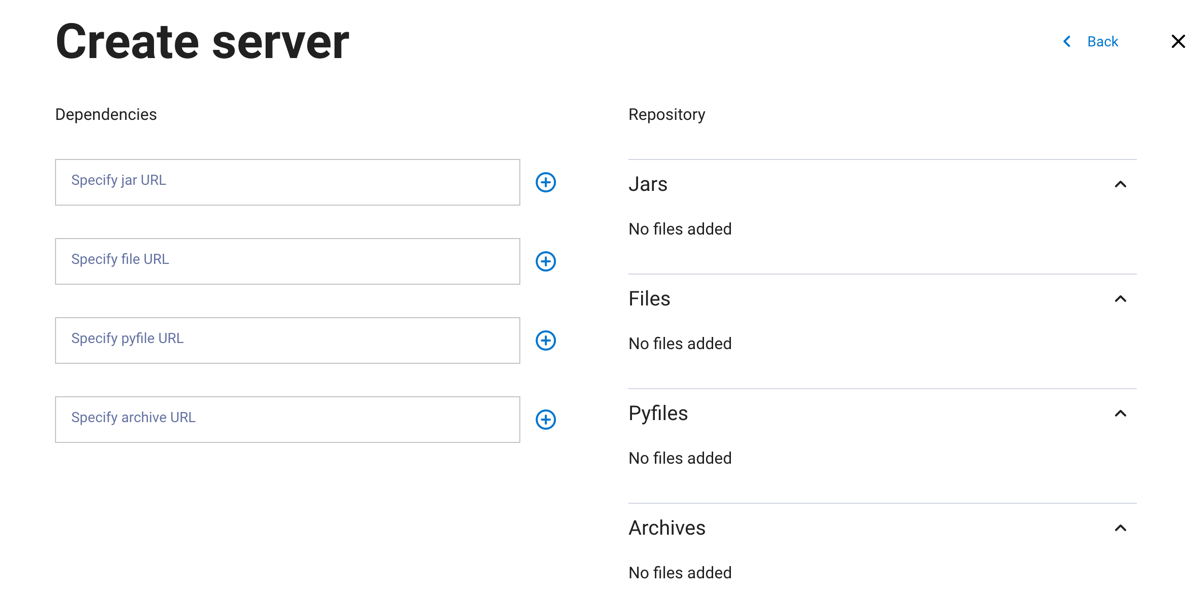
Add the path for your server’s dependencies. Dependencies can be
JAR,FILES,PYFILES, orARCHIVEfiles. Click + to add more dependencies of the same file type. Files are displayed on the right side of the pane.Click Create.
Delete Spark Connect server#
To delete a server, click the options menu for the server and select Delete server.
Jupyter Notebook servers#
Dell Data Processing Engine supports Jupyter Notebook servers, offering fast and interactive ways to explore your data. Users can view the Notebook interface from the Notebook servers tab. Access to the Notebook servers depend on the Jupyter Notebook privileges a user’s role has.
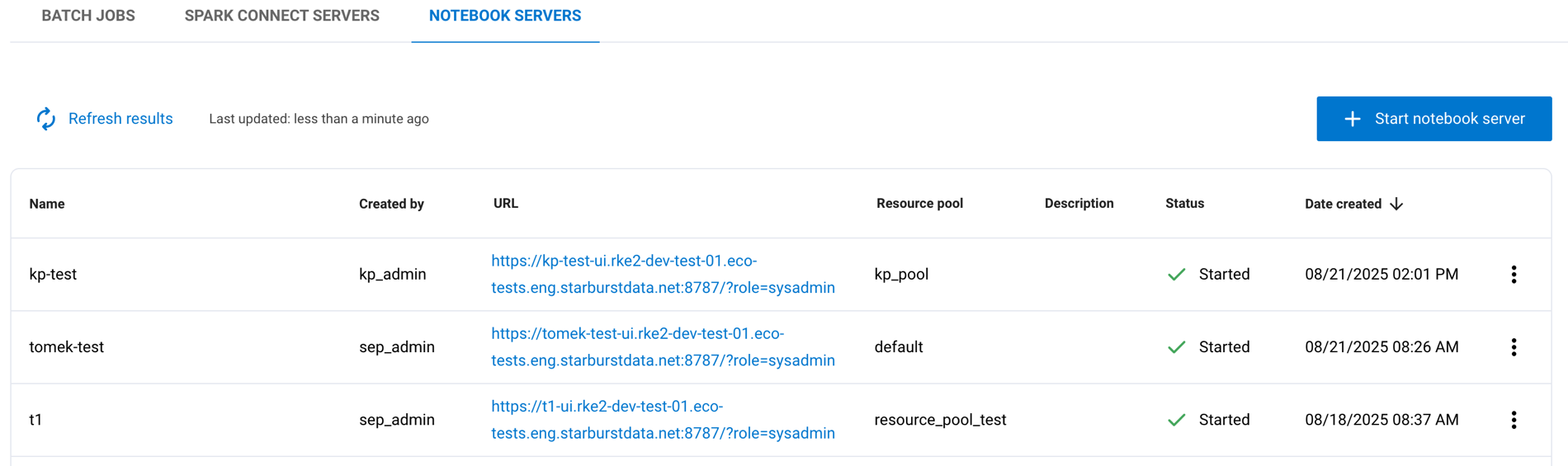
The following information is displayed about your Notebook servers:
Name: The name given to the server.
Created by: The user who created the server.
URL: The web address to access the server.
Resource pool: The resource pool allocated to the server.
Description: Additional information or notes about the server.
Status: The current state of the server, such as
StartedorShutdown.Date created: The timestamp for when the server was created.
Click the options menu for a server to perform additional actions such as starting a shutdown server, shutting down a running server, downloading logs, or deleting the server:
Jupyter Notebook privileges#
The following table lists privileges users must have to execute various Jupyter Notebook-related tasks:
Privilege |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Start Notebook server#
Click + Start Notebook server to open a dialog to launch a new server:
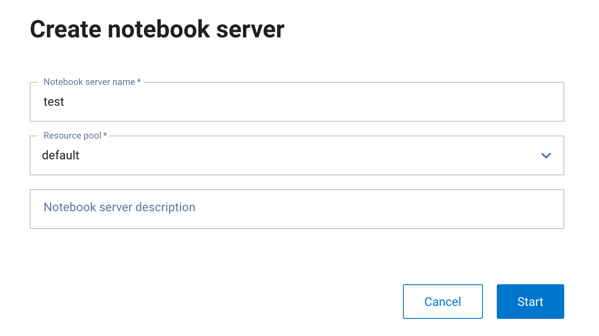
Give the server a name, assign a resource pool, and optionally provide a description. Click Start.
The new server displays in the server list with a Pending status for a few
moments before the URL column populates and the server is moved to the
Started status. Click the URL to open the server:
Delete Notebook server#
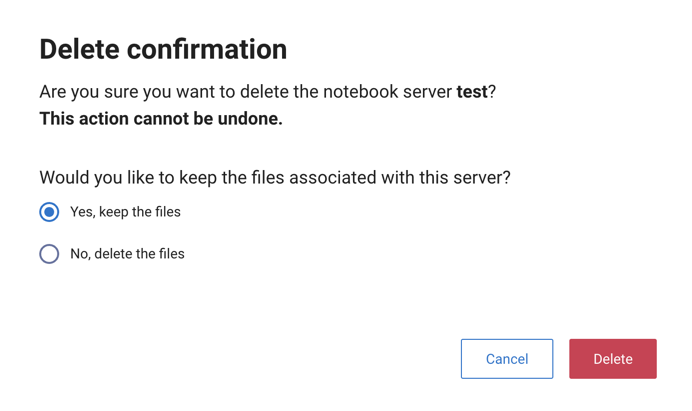
To delete an existing Jupyter Notebook server, open the options menu for a server, choose whether to keep the files associate with this server or not, and click Delete:
Notebook example#
The following shows a basic workflow for using Spark in a Jupyter Notebook:
Initiate your notebook with
SparkSession:from pyspark.sql import SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder \ .remote("sc://sj-iceberg-cpu-grpc.rke2-dev-test-01.eco-tests.eng.starburstdata.net:8787/token=eyJraWQ101J0ZXN0aW5nIiwidHlwIjoiSldUIiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyN ...") \ .getOrCreate()
After you have created your
SparkSession, you can initialize and work with Spark DataFrames, such as the following:Create a DataFrame:
data = [("Alice", 34), ("Bob", 45), ("Cathy", 29)] columns = ["Name", "Age"] df = spark.createDataFrame(data, columns)
Show the DataFrame contents:
df.show()
+-----+---+ | Name|Age| +-----+---+ |Alice| 34| | Bob| 45| |Cathy| 29| +-----+---+
Perform a basic transformation:
df_filtered = df.filter(df.Age > 30) df_filtered.show()
+-----+---+ | Name|Age| +-----+---+ |Alice| 34| | Bob| 45| +-----+---+
View the official Jupyter Notebook documentation for more details.